BIS Certification for Hot-Dip Zinc Coating on Structural Steel and Allied Products IS 4759:1996

Corrosion is one of the most
persistent threats to the integrity and longevity of steel structures. In
industries like construction, transportation, energy, and manufacturing,
protecting steel from rust is essential not just for durability but also for
safety and cost-effectiveness. Hot-dip
galvanizing, a widely accepted method of corrosion protection, plays a
crucial role in addressing this challenge.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), through its standard IS 4759:1996, regulates the hot-dip zinc coating process for structural steel and other allied products in India. This standard sets comprehensive guidelines for quality, testing, and application of zinc coatings to ensure that galvanized steel products meet the requirements for performance, durability, and safety.
What Is Hot-Dip Zinc
Coating?
Hot-dip galvanizing is a metallurgical
process where steel or iron products are
immersed in molten zinc, resulting in a tightly bonded, corrosion-resistant
coating. This process forms multiple layers of zinc-iron alloy between the base steel and the outer layer of pure
zinc. The result is a highly durable protective barrier that shields the steel
from environmental elements such as moisture, oxygen, and pollutants.
This method is particularly suited for structural steel used in bridges, towers, pipelines, building frameworks, power transmission structures, railways, and a wide range of industrial applications exposed to weather or corrosive environments.
IS 4759:1996 – An Overview
Indian Standard IS 4759:1996, titled “Hot-Dip
Zinc Coatings on Structural Steel and Other Allied Products – Specification”,
lays out detailed provisions for the galvanizing process, from material
selection to testing criteria. The standard applies to a variety of products,
including structural shapes, plates, pipes, and fabricated steel items.
Key Aspects
Covered:
Importance of BIS
Certification
Obtaining BIS certification under IS 4759:1996 is mandatory for manufacturers
and suppliers who wish to market hot-dip galvanized steel products in India
under regulatory compliance. Certification ensures that:
Moreover, certified products are often a prerequisite in government tenders and large infrastructure projects, making BIS certification commercially vital.
Testing and Quality
Assurance
To ensure that galvanized products
meet the requirements of IS 4759:1996, BIS mandates a series of quality tests.
These tests are typically conducted during the certification process and at
regular intervals thereafter.
Core Tests
Include:
All testing is carried out at BIS-approved laboratories or in-house facilities certified under the BIS Laboratory Recognition Scheme.
BIS Certification Process for Manufacturers
Manufacturers seeking BIS
certification under IS 4759:1996 must undergo the following process:
- Application Submission: Provide technical documents, manufacturing details, and process flow related to galvanizing.
- Product Sampling & Testing: Samples are taken and tested as per IS 4759 specifications.
- Factory Audit: BIS officials inspect the facility for quality control practices, production capabilities, and testing infrastructure.
- Grant of Certification: Upon successful evaluation, BIS grants a license to use the ISI Mark on compliant products.
- Surveillance & Renewal: Periodic factory audits and retesting ensure continuous compliance.
To Know The Process in Detail, Please Visit:
Under BIS Registration Products ISI and CRS
Documents Required for BIS Certification
To apply for BIS certification, manufacturers need to submit the following documents:
● Application form
● Manufacturing process details
● Quality control plan
● Test reports from BIS-approved laboratories
● Factory layout and equipment details
● Proof of business registration
● Product specifications and technical details
● Declaration of conformity to Indian standards
Additionally, manufacturers may be required to provide proof of compliance with environmental and safety regulations, depending on the specific type of product being certified.
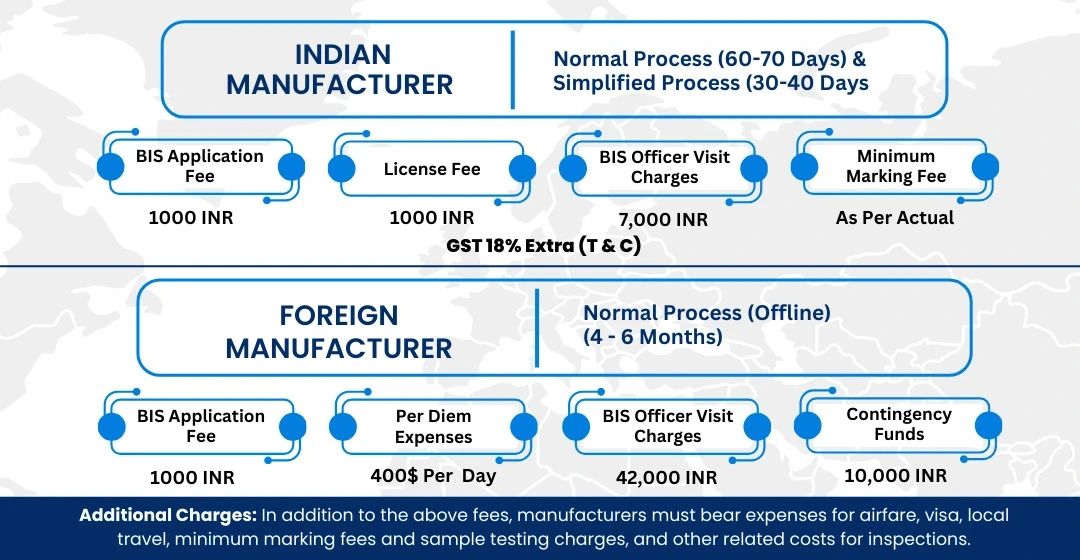
BIS ISI Mark Certification Costing And Timeline
Conclusion
As India rapidly expands its
infrastructure footprint, the demand for durable and corrosion-resistant steel
products is growing. Hot-dip galvanized steel, regulated under IS 4759:1996,
plays a vital role in meeting this need. BIS certification ensures that the
products used in critical projects—from highways to power grids—are not only
structurally sound but also built to last.
For manufacturers and suppliers,
compliance with IS 4759 is not just about meeting a regulatory requirement—it's
about demonstrating commitment to quality, safety, and performance.
Free Call Back
Latest News & Update
📅 BIS Critical Component List (CCL) Updates for Solar PV Modules
🕒 BIS Fee Concessions for MSMEs and Startups | EVTL India
📅 Guidelines for Implementation of Essential Requirements for Security of CCTV
🕒 Omnibus Technical Regulation (OTR) Amendment Order, 2025
🕒 Extension of Timeline for Filing Annual Returns by Battery Producers
📅 Extension of Timeline for Filing Quarterly and Annual Returns for E-Waste
🕒 Extension of Concurrent Running Period for IS 302-1: 2008 and IS 302 (Part 1): 2024
🕒 BIS Guidelines for Grant of Licence (GoL) | EVTL India
📅 CPCB Guidance on filing of Application, Fees and more
🕒 CPCB Notification on Labelling of Plastic Packaging
📅 Mandatory Compliance for Input Materials of Steel and Steel Products for Imports
🕒 BIS Guidelines for Scheme-X Certification for OTR-Regulated Products
📅 BIS Upgrades Product Certification License Numbers to 10-Digit Series
Why Choose EVTL INDIA
Expertise in Indian Regulatory Standards
End-to-End Support
Trusted by Top Indian & Global Brands
Fast Processing & Transparent Pricing
Strong Liaison with Indian Authorities
Company Profile